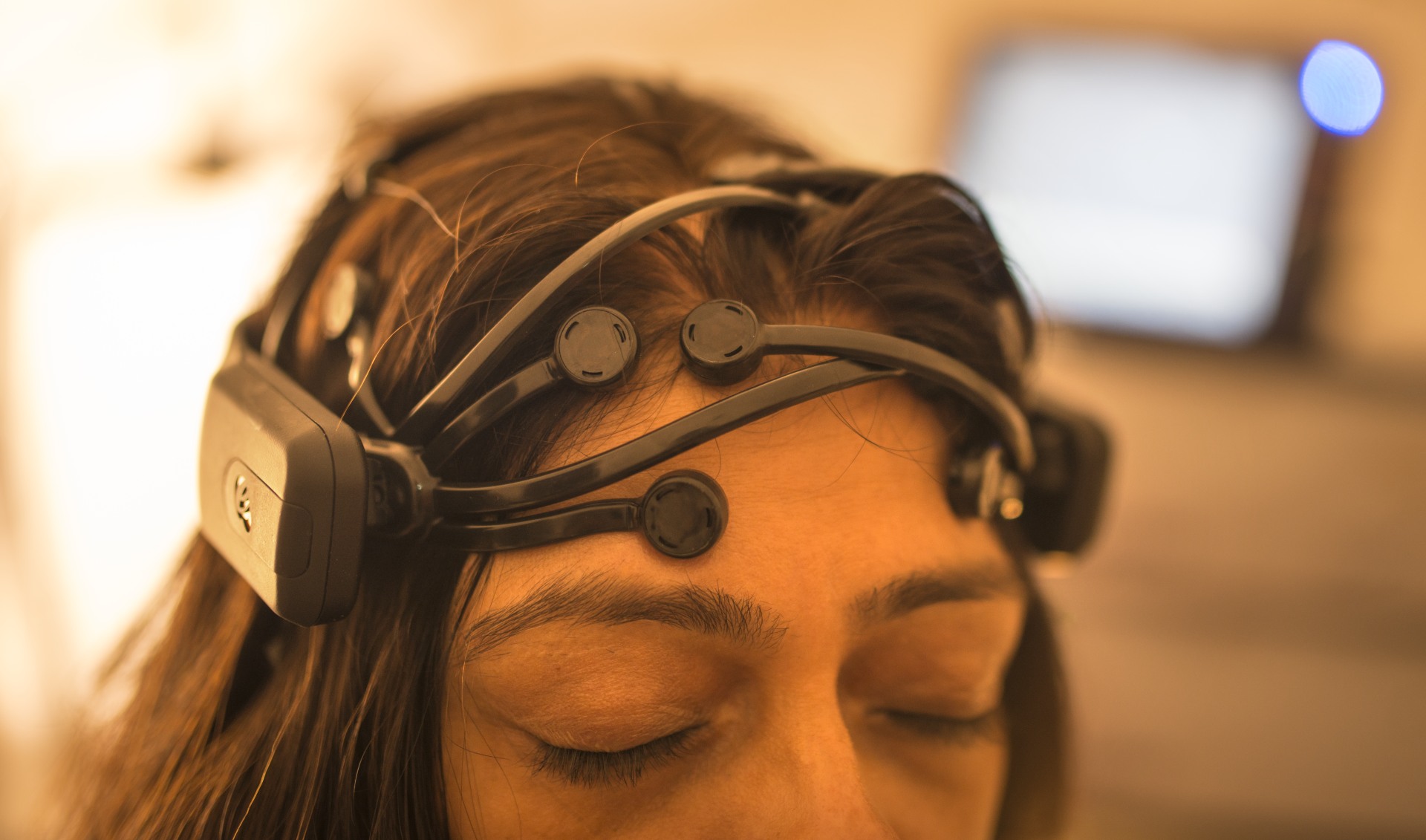
What is tDCS?
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation or tDCS is a Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation technique in which a device sends a small Direct Current (DC) derived from a small 9V battery across the scalp to modulate brain function. Electrodes (sponges soaked in salt water) are placed over certain parts of the head. The electrodes are held in place using a headband. The direct current flows through the electrodes, penetrating the scalp, creating a flow of electrical current in the brain. Usually a slight itching or tingling sensation can be felt on the scalp in the first few seconds. The weak currents enhance brain activity under the site of the electrodes.
What are the indications for tDCS?
tDCS is considered to safely induce reversible changes in neuron excitation and can induce benefits in various conditions, such as:
- Treatment of depression
- Anxiety Disorders
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Fibromyalgia
- Chronic neuropathic pain
- Migraine
- Chronic Headache
- Parkinsonism
- Post- Stroke recovery
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Enhancement of Learning
- Enhancement of Cognitive Skills such as Attention and Memory
- Enhancement of Language and Mathematical Ability
What are the effects of tDCS on the brain?

One of the most important aspects of tDCS is its ability to achieve and cause sustained cortical (brain activity) changes even after the stimulation is ended. The duration of this change depends on the length of stimulation as well as the intensity of current.
What are the unique features of tDCS?
Safety, ease of use and general absence of severe side effects are the unique features of tDCS. This significantly reduces costs, increases accessibility to treatment, gives the option of longer treatment protocols and continuity of treatment is more easily maintained.
What are the adverse effects of tDCS?
tDCS is an extremely safe technique. The most common report by clients is that of a tingling sensation under the electrodes. This transient sensation is present during and shortly after the period of stimulation for a few seconds and has no adverse effects or risks. Almost all clients have reported the sensation as quite mild.